 核心内容拆解 IOC
核心内容拆解 IOC
Spring 是 JAVA 开发用到最多的一个 WEB 框架,核心是 IOC(控制反转)和 AOP(面向切面),但做为架构,想要对 Spring 要进行扩展等,必须要了解 Spring 的生命周期、事件、AOP、行为感知等。Spring 生命周期如下图:
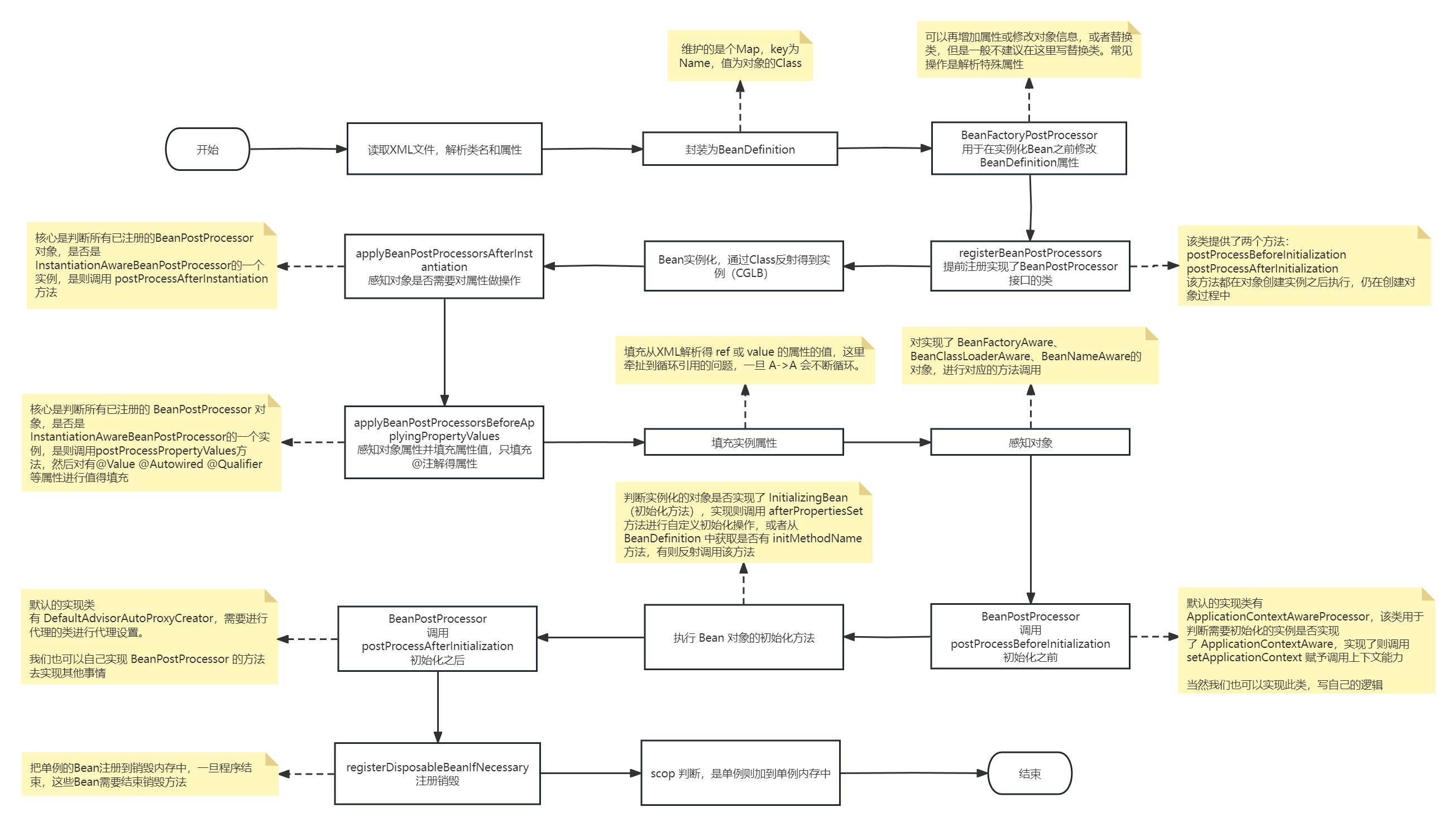
提示
本文主要了解 spring 生命周期的有哪些,以及他们的核心代码是怎么编写,整个过程是偏 IOC 和 DI 的,IOC 将对象的创建和依赖关系的维护从代码中脱离出来,通过配置读取创建对象;DI 从注解属性填充过程以及 XML 属性填充过程为具体的体现。
# 读取 XML 文件
通过 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 来读取资源文件下的 spring.xml
@Test
public void test() {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println("测试结果:" + userService.queryUserInfo());
}
2
3
4
5
6
根据文件类型使用不同的方式读取到流中
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
Assert.notNull(location, "Location must not be null");
if (location.startsWith(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX)) {
return new ClassPathResource(location.substring(CLASSPATH_URL_PREFIX.length()));
}
else {
try {
URL url = new URL(location);
return new UrlResource(url);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
return new FileSystemResource(location);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
调用 XML 解析
@Override
public void loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeansException {
try {
try (InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream()) {
doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputStream);
}
} catch (IOException | ClassNotFoundException | DocumentException e) {
throw new BeansException("IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, e);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 封装 BeanDefinition
解析 XML 的整个过程:
- 解析 DOM
- 解析带有 @Component 注解的类,并封装为 BeanDefinition 注册到 BeanFactory
- 解析不是 component-scan 定义的类
protected void doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputStream inputStream) throws ClassNotFoundException, DocumentException {
// 使用 org.dom4j.io 的解析器
SAXReader reader = new SAXReader();
Document document = reader.read(inputStream);
Element root = document.getRootElement();
// 解析 context:component-scan 标签,扫描包中的类并提取相关信息,用于组装 BeanDefinition
Element componentScan = root.element("component-scan");
if (null != componentScan) {
String scanPath = componentScan.attributeValue("base-package");
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(scanPath)) {
throw new BeansException("The value of base-package attribute can not be empty or null");
}
// 扫描整个包
scanPackage(scanPath);
}
List<Element> beanList = root.elements("bean");
for (Element bean : beanList) {
String id = bean.attributeValue("id");
String name = bean.attributeValue("name");
String className = bean.attributeValue("class");
String initMethod = bean.attributeValue("init-method");
String destroyMethodName = bean.attributeValue("destroy-method");
String beanScope = bean.attributeValue("scope");
// 获取 Class,方便获取类中的名称
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 优先级 id > name
String beanName = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(id) ? id : name;
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(beanName)) {
beanName = StrUtil.lowerFirst(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
// 定义Bean
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition(clazz);
beanDefinition.setInitMethodName(initMethod);
beanDefinition.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(beanScope)) {
beanDefinition.setScope(beanScope);
}
List<Element> propertyList = bean.elements("property");
// 读取属性并填充
for (Element property : propertyList) {
// 解析标签:property
String attrName = property.attributeValue("name");
String attrValue = property.attributeValue("value");
String attrRef = property.attributeValue("ref");
// 获取属性值:引入对象、值对象
Object value = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(attrRef) ? new BeanReference(attrRef) : attrValue;
// 创建属性信息
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(attrName, value);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
if (getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
throw new BeansException("Duplicate beanName[" + beanName + "] is not allowed");
}
// 注册 BeanDefinition
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
}
private void scanPackage(String scanPath) {
String[] basePackages = StrUtil.splitToArray(scanPath, ',');
ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(getRegistry());
scanner.doScan(basePackages);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
根据提供路径封装为 BeanDefinition 并注册到 BeanFactory
public void doScan(String... basePackages) {
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = findCandidateComponents(basePackage);
for (BeanDefinition beanDefinition : candidates) {
// 解析 Bean 的作用域 singleton、prototype
String beanScope = resolveBeanScope(beanDefinition);
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(beanScope)) {
beanDefinition.setScope(beanScope);
}
registry.registerBeanDefinition(determineBeanName(beanDefinition), beanDefinition);
}
}
// 注册处理注解的 BeanPostProcessor(@Autowired、@Value)
registry.registerBeanDefinition("cn.bugstack.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor", new BeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
对提供的包路径扫描有 @Component 注解的类
public Set<BeanDefinition> findCandidateComponents(String basePackage) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<>();
Set<Class<?>> classes = ClassUtil.scanPackageByAnnotation(basePackage, Component.class);
for (Class<?> clazz : classes) {
candidates.add(new BeanDefinition(clazz));
}
return candidates;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# BeanFactoryPostProcessor
BeanFactoryPostProcessor 可以修改我们对 BeanDefinition 定义的所有信息,可以添加属性,修改属性,添加额外的方法等。具体会对所有实现 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 的类进行获取,并循环调用 postProcessBeanFactory 方法
private void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Map<String, BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessorMap = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class);
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor beanFactoryPostProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessorMap.values()) {
beanFactoryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
提供一个默认的实现
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
// 加载属性文件
DefaultResourceLoader resourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
// 把属性文件的内容加载到Properties里组成键值对
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.load(resource.getInputStream());
String[] beanDefinitionNames = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String beanName : beanDefinitionNames) {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
PropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
Object value = propertyValue.getValue();
if (!(value instanceof String)) continue;
value = resolvePlaceholder((String) value, properties);
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(new PropertyValue(propertyValue.getName(), value));
}
}
// 向容器中添加字符串解析器,供解析@Value注解使用
StringValueResolver valueResolver = new PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver(properties);
// 注册到容器,以便后续使用
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new BeansException("Could not load properties", e);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 注册实现 BeanPostProcessor 的类
BeanPostProcessor 就是提供了 postProcessBeforeInitialization,postProcessAfterInitialization 两种方法,提供我们在实例化 Bean 的时候,所有实现 BeanPostProcessor 的类,注册到 List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanPostProcessor>(); 中
private void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Map<String, BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessorMap = beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanPostProcessor.class);
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : beanPostProcessorMap.values()) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(beanPostProcessor);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
# 实例化 Bean
protected <T> T doGetBean(final String name, final Object[] args) {
// 从缓存中获取实例
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(name);
if (sharedInstance != null) {
// 如果实现了 FactoryBean,则需要调用 FactoryBean##getObject
return (T) getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name);
}
// 从BeanDefinition列表中获取对象
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = getBeanDefinition(name);
Object bean = createBean(name, beanDefinition, args);
// 如果实现了 FactoryBean,则需要调用 FactoryBean##getObject
return (T) getObjectForBeanInstance(bean, name);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
实例化 Bean 的具体方法
protected Object doCreateBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition, Object[] args) {
Object bean = null;
try {
// 实例化 Bean
bean = createBeanInstance(beanDefinition, beanName, args);
// 处理循环依赖,将实例化后的Bean对象提前放入缓存中暴露出来
if (beanDefinition.isSingleton()) {
Object finalBean = bean;
addSingletonFactory(beanName, () -> getEarlyBeanReference(beanName, beanDefinition, finalBean));
}
// 是否需要继续进行后续的属性填充
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInstantiation(beanName, bean);
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return bean;
}
// 在设置 Bean 属性之前,允许 BeanPostProcessor 修改属性值(注解属性填充)
applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeApplyingPropertyValues(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
// 给 Bean 填充属性(xml属性填充)
applyPropertyValues(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
// 执行 Bean 的初始化方法和 BeanPostProcessor 的前置和后置处理方法
bean = initializeBean(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Instantiation of bean failed", e);
}
// 注册实现了 DisposableBean 接口的 Bean 对象
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
// 判断 SCOPE_SINGLETON、SCOPE_PROTOTYPE
Object exposedObject = bean;
if (beanDefinition.isSingleton()) {
// 获取代理对象
exposedObject = getSingleton(beanName);
registerSingleton(beanName, exposedObject);
}
return exposedObject;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
createBeanInstance 使用了 CGLIB 来实例化一个 Bean, 也可以使用 JAVA 自带的反射
protected Object createBeanInstance(BeanDefinition beanDefinition, String beanName, Object[] args) {
Constructor constructorToUse = null;
Class<?> beanClass = beanDefinition.getBeanClass();
Constructor<?>[] declaredConstructors = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();
for (Constructor ctor : declaredConstructors) {
if (null != args && ctor.getParameterTypes().length == args.length) {
constructorToUse = ctor;
break;
}
}
return getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate(beanDefinition, beanName, constructorToUse, args);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
CGLIB 实现实例化
@Override
public Object instantiate(BeanDefinition beanDefinition, String beanName, Constructor ctor, Object[] args) throws BeansException {
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
enhancer.setSuperclass(beanDefinition.getBeanClass());
enhancer.setCallback(new NoOp() {
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return super.hashCode();
}
});
if (null == ctor) return enhancer.create();
return enhancer.create(ctor.getParameterTypes(), args);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
JAVA 反射实现序列化
@Override
public Object instantiate(BeanDefinition beanDefinition, String beanName, Constructor ctor, Object[] args) throws BeansException {
Class clazz = beanDefinition.getBeanClass();
try {
if (null != ctor) {
return clazz.getDeclaredConstructor(ctor.getParameterTypes()).newInstance(args);
} else {
return clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
}
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
throw new BeansException("Failed to instantiate [" + clazz.getName() + "]", e);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 注解属性填充
注解属性,会从之前注册的 BeanPostProcessor 里匹配 InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的对象,其中默认的 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 具体实现了该类
protected void applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeApplyingPropertyValues(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
for (BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (beanPostProcessor instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
PropertyValues pvs = ((InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) beanPostProcessor).postProcessPropertyValues(beanDefinition.getPropertyValues(), bean, beanName);
if (null != pvs) {
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : pvs.getPropertyValues()) {
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 感知注解属性填充
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Class<?> clazz = bean.getClass();
clazz = ClassUtils.isCglibProxyClass(clazz) ? clazz.getSuperclass() : clazz;
// 获得对象所有字段
Field[] declaredFields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
// @Value 注解
Value valueAnnotation = field.getAnnotation(Value.class);
if (null != valueAnnotation) {
Object value = valueAnnotation.value();
// 解析得到值
value = beanFactory.resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value);
// 类型转换
Class<?> sourceType = value.getClass();
Class<?> targetType = (Class<?>) TypeUtil.getType(field);
// 对值进行转换处理
ConversionService conversionService = beanFactory.getConversionService();
if (conversionService != null) {
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceType, targetType)) {
value = conversionService.convert(value, targetType);
}
}
// 把值设置进去
BeanUtil.setFieldValue(bean, field.getName(), value);
}
}
// 2. 处理注解 @Autowired
for (Field field : declaredFields) {
Autowired autowiredAnnotation = field.getAnnotation(Autowired.class);
if (null != autowiredAnnotation) {
Class<?> fieldType = field.getType();
String dependentBeanName = null;
Qualifier qualifierAnnotation = field.getAnnotation(Qualifier.class);
Object dependentBean = null;
if (null != qualifierAnnotation) {
dependentBeanName = qualifierAnnotation.value();
dependentBean = beanFactory.getBean(dependentBeanName, fieldType);
} else {
dependentBean = beanFactory.getBean(fieldType);
}
BeanUtil.setFieldValue(bean, field.getName(), dependentBean);
}
}
return pvs;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
# XML 属性填充
XML 属性填充这里说过会出现循环依赖的问题,在实例化阶段的前后已经对这个处理了,后续会单独讲解
protected void applyPropertyValues(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
try {
PropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValues.getPropertyValues()) {
String name = propertyValue.getName();
Object value = propertyValue.getValue();
if (value instanceof BeanReference) {
// A 依赖 B,获取 B 的实例化
BeanReference beanReference = (BeanReference) value;
value = getBean(beanReference.getBeanName());
}
// 类型转换
else {
Class<?> sourceType = value.getClass();
Class<?> targetType = (Class<?>) TypeUtil.getFieldType(bean.getClass(), name);
ConversionService conversionService = getConversionService();
if (conversionService != null) {
if (conversionService.canConvert(sourceType, targetType)) {
value = conversionService.convert(value, targetType);
}
}
}
// 反射设置属性填充
BeanUtil.setFieldValue(bean, name, value);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Error setting property values:" + beanName + " message:" + e);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
# 感知对象
感知对象做为一个扩展接口,只要我们的 Bean 实现了这些接口,就可以为我们的 Bean 提供额外的能力
private Object initializeBean(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
// invokeAwareMethods(感知对象)
if (bean instanceof Aware) {
if (bean instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) bean).setBeanFactory(this);
}
if (bean instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) bean).setBeanClassLoader(getBeanClassLoader());
}
if (bean instanceof BeanNameAware) {
((BeanNameAware) bean).setBeanName(beanName);
}
}
// 1. 执行 BeanPostProcessor Before 处理
Object wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(bean, beanName);
// 执行 Bean 对象的初始化方法
try {
invokeInitMethods(beanName, wrappedBean, beanDefinition);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Invocation of init method of bean[" + beanName + "] failed", e);
}
// 2. 执行 BeanPostProcessor After 处理
wrappedBean = applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(wrappedBean, beanName);
return wrappedBean;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
# 初始化方法之前
在 Bean 的初始化方法之前调用,默认提供了 applicationContext 的上下文注入,当某个类实现了 ApplicationContextAware,就提供 applicationContext 上下文的能力,只是我们要实现的是 ApplicationContextAware ,并不是 BeanPostProcessor
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessBeforeInitialization(result, beanName);
if (null == current) return result;
result = current;
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean instanceof ApplicationContextAware){
((ApplicationContextAware) bean).setApplicationContext(applicationContext);
}
return bean;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
# Bean 的初始化方法
Bean 初始化方法还是比较简单的,主要是通过判断是否实现 InitializingBean 接口,如果实现了,则调用实例化对象实现的 afterPropertiesSet 方法。如果不是以接口实现的,是以 XML 描述的,则是通过反射的方式调用该方法。
private void invokeInitMethods(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) throws Exception {
// 1. 实现接口 InitializingBean
if (bean instanceof InitializingBean) {
((InitializingBean) bean).afterPropertiesSet();
}
// 2. 注解配置 init-method {判断是为了避免二次执行销毁}
String initMethodName = beanDefinition.getInitMethodName();
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(initMethodName)) {
Method initMethod = beanDefinition.getBeanClass().getMethod(initMethodName);
if (null == initMethod) {
throw new BeansException("Could not find an init method named '" + initMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
initMethod.invoke(bean);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
<bean id="userDao" class="cn.bugstack.springframework.test.bean.UserDao" init-method="initDataMethod" destroy-method="destroyDataMethod"/>
# 初始化方法之后
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (null == current) return result;
result = current;
}
return result;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 注册销毁事件
销毁事件需要 Bean 实现 DisposableBean 接口并重写 destroy () 方法。如下先是把实现 DisposableBean 或有在 XML 描述过销毁方法的注册到一个容器里。
protected void registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(String beanName, Object bean, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
// 非 Singleton 类型的 Bean 不执行销毁方法
if (!beanDefinition.isSingleton()) return;
if (bean instanceof DisposableBean || StrUtil.isNotEmpty(beanDefinition.getDestroyMethodName())) {
registerDisposableBean(beanName, new DisposableBeanAdapter(bean, beanName, beanDefinition));
}
}
public void registerDisposableBean(String beanName, DisposableBean bean) {
disposableBeans.put(beanName, bean);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
然后再整个启动过程结束调用 registerShutdownHook 方法添加一个钩子监听。
@Override
public void registerShutdownHook() {
// Java 中的一个方法,它用于注册 JVM 关闭时要执行的特定代码块。当 JVM 即将关闭时,这些代码块会被执行,以便进行清理、释放资源等操作。
// 这些代码块通常称为“钩子(hook)”,因此该方法也被称为“添加关闭钩子(Add Shutdown Hook)”。
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(this::close));
}
@Override
public void close() {
// 发布容器关闭事件
publishEvent(new ContextClosedEvent(this));
// 执行销毁单例bean的销毁方法
getBeanFactory().destroySingletons();
}
public void destroySingletons() {
Set<String> keySet = this.disposableBeans.keySet();
Object[] disposableBeanNames = keySet.toArray();
for (int i = disposableBeanNames.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
Object beanName = disposableBeanNames[i];
DisposableBean disposableBean = disposableBeans.remove(beanName);
try {
disposableBean.destroy();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Destroy method on bean with name '" + beanName + "' threw an exception", e);
}
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// 1. 实现接口 DisposableBean
if (bean instanceof DisposableBean) {
((DisposableBean) bean).destroy();
}
// 2. 注解配置 destroy-method {判断是为了避免二次执行销毁}
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(destroyMethodName) && !(bean instanceof DisposableBean && "destroy".equals(this.destroyMethodName))) {
Method destroyMethod = bean.getClass().getMethod(destroyMethodName);
if (null == destroyMethod) {
throw new BeansException("Couldn't find a destroy method named '" + destroyMethodName + "' on bean with name '" + beanName + "'");
}
destroyMethod.invoke(bean);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
# scop 处理单例
public void registerSingleton(String beanName, Object singletonObject) {
// 三级缓存
singletonObjects.put(beanName, singletonObject);
// 二级缓存
earlySingletonObjects.remove(beanName);
// 一级缓存
singletonFactories.remove(beanName);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
