 核心功能拆解 一二级缓存原理
核心功能拆解 一二级缓存原理
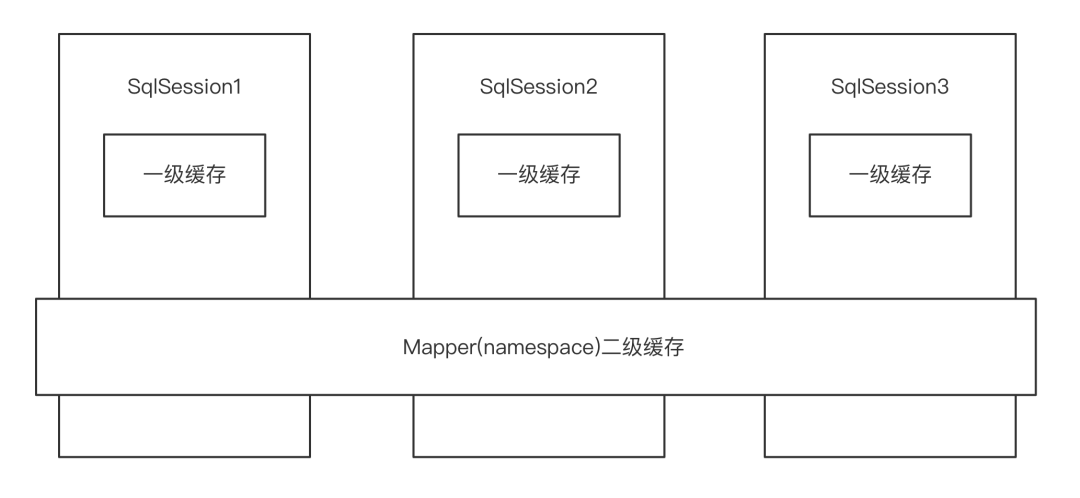
MyBatis 的缓存分为一级缓存和二级缓存,缓存情况如下图,单服务架构中(有且仅有只有一个程序提供相同服务),一级缓存开启不会影响业务,只会提高性能。 微服务架构中需要关闭一级缓存,原因:Service1 先查询数据,若之后 Service2 修改了数据,之后 Service1 又再次以同样的查询条件查询数据,因走缓存会出现查处的数据不是最新数据
# 一级缓存
一级缓存是基于 SQLSession 级别的,在同一个 Session 的相同查询语句会才会从缓存中查询,所谓相同包括 SQL 相同,条件相同等,那么我们看下在源码中具体是怎么维护和使用这个缓存的。
# 解析
描述一级缓存只需要在 <configuration> 标签中描述即可,而一级缓存的 value 值有 SESSION 和 STATEMENT 两种,如果设置为 STATEMENT 关闭一级缓存,一级缓存是 MyBatis 提供的默认缓存
<configuration>
<settings>
<!--缓存级别:SESSION/STATEMENT-->
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
2
3
4
5
6
解析核心代码会得到 localCacheScope的值 ,维护到 configuration 全局配置中
private void settingsElement(Element context) {
if (context == null) return;
List<Element> elements = context.elements();
Properties props = new Properties();
for (Element element : elements) {
props.setProperty(element.attributeValue("name"), element.attributeValue("value"));
}
// 是否启用二级缓存
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
// 一级缓存的配置
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope")));
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 准备
准备阶段主要是在 openSession 方法,他会在执行器里面去直接 new PerpetualCache 永久缓存,执行器就拥有了这个缓存对象
// 打开一个 session
@Override
public SqlSession openSession() {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
TransactionFactory transactionFactory = environment.getTransactionFactory();
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(configuration.getEnvironment().getDataSource(), TransactionIsolationLevel.READ_COMMITTED, false);
// 创建执行器
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx);
// 创建DefaultSqlSession
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor);
} catch (Exception e) {
try {
assert tx != null;
tx.close();
} catch (SQLException ignore) {
}
throw new RuntimeException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e);
}
}
// 创建执行器
public Executor newExecutor(Transaction transaction) {
Executor executor = new SimpleExecutor(this, transaction);
// 配置开启二级缓存,创建 CachingExecutor(默认就是有缓存)装饰者模式,
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
return executor;
}
// SimpleExecutor 简单执行器的构造方法
public class SimpleExecutor extends BaseExecutor {
public SimpleExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
super(configuration, transaction);
}
}
// 基础执行器的构造方法
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.transaction = transaction;
this.wrapper = this;
// new 一个永久缓存
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
PerpetualCache 继承了 Cache ,并实现了基本的对缓存的操作
public class PerpetualCache implements Cache {
private String id;
// 使用HashMap存放一级缓存数据,session 生命周期较短,正常情况下数据不会一直在缓存存放
private Map<Object, Object> cache = new HashMap<>();
public PerpetualCache(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return id;
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object value) {
cache.put(key, value);
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
return cache.get(key);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return cache.remove(key);
}
@Override
public void clear() {
cache.clear();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return cache.size();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
# 执行
在准备阶段已经得到了执行器,并在执行器里面得到了 PerpetualCache 缓存,只需要知道客户使用的是查询还是修改等操作后,执行执行器里面对应的 query or update 方法即可,核心看 query
public abstract class BaseExecutor implements Executor {
private org.slf4j.Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(BaseExecutor.class);
protected Configuration configuration;
protected Transaction transaction;
protected Executor wrapper;
// 本地缓存
protected PerpetualCache localCache;
private boolean closed;
// 查询堆栈
protected int queryStack = 0;
protected BaseExecutor(Configuration configuration, Transaction transaction) {
this.configuration = configuration;
this.transaction = transaction;
this.wrapper = this;
this.localCache = new PerpetualCache("LocalCache");
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Executor was closed.");
}
clearLocalCache();
return doUpdate(ms, parameter);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 1. 获取绑定SQL
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 2. 创建缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Executor was closed.");
}
// 清理局部缓存,查询堆栈为0则清理。queryStack 避免递归调用清理
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List<E> list;
try {
queryStack++;
// 根据cacheKey从localCache中查询数据
list = resultHandler == null ? (List<E>) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list == null) {
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
// 如果不是 SESSION 模式,则清除缓存
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private <E> List<E> queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List<E> list;
localCache.putObject(key, ExecutionPlaceholder.EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
// 存入缓存
localCache.putObject(key, list);
return list;
}
protected abstract int doUpdate(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException;
protected abstract <E> List<E> doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException;
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Executor was closed.");
}
return transaction;
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Cannot commit, transaction is already closed");
}
clearLocalCache();
if (required) {
transaction.commit();
}
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
if (!closed) {
try {
clearLocalCache();
} finally {
if (required) {
transaction.rollback();
}
}
}
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
if (!closed) {
localCache.clear();
}
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new RuntimeException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
@Override
public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor) {
this.wrapper = wrapper;
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
try {
rollback(forceRollback);
} finally {
transaction.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
logger.warn("Unexpected exception on closing transaction. Cause: " + e);
} finally {
transaction = null;
localCache = null;
closed = true;
}
}
protected void closeStatement(Statement statement) {
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException ignore) {
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
可以看到 执行器里面维护了 query update commit 等方法,在执行查询的时候会先生成 CacheKey ,会按照 namespace.id + 分页offset + 分页limit + 执行的SQL语句 + 查询条件的值 + 环境ID 生成唯一的 key,然后做为查询缓存的 key,查询结果做为 value,如果同一各 SQLSession 执行相同语句和条件以及分页等,就会从缓存中命中并返回结果。缓存的清除,就是当该 SQLSession 执行 update,commit,close,rollback 时该 SQLSession 就清除缓存。
在 SQL 语句中也可以设置清除缓存,只需要在 <select>、<insert> 和 <update> 等 SQL 标签中设置 flushCache="true" 属性会强制清空本地缓存,使得下次查询时重新从数据库中获取数据。适用于一级缓存和二级缓存
<select id="selectById" resultType="com.example.User" flushCache="true">
select * from user where id = #{id}
</select>
2
3
还有就是在 query 查询中,当如果你设置 LocalCacheScope = STATEMENT 时,在 query 也会自动清除缓存,也就是我们所说的关闭一级缓存的方法
# 二级缓存
二级缓存是为 Namespace 也叫 mapper 级别的缓存,是跨 SQLSession 的,他会在原有的执行器上封装一个 CachingExecutor ,来管理缓存, CachingExecutor 使用了装饰器模式来装饰基础的 Executor 执行器。
# 解析
在二级缓存中的配置方式具体如下
<!-- 必须先开启缓存 -->
<configuration>
<settings>
<!-- true/false 二级缓存是否使用 -->
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
<!-- 指定在某个mapper中使用 -->
<mapper namespace="com.example.MyMapper">
<!-- 设置该mapper的二级缓存 -->
<cache eviction="LRU" flushInterval="100000" readOnly="true" size="1024"/>
<!-- useCache:表示是否使用二级缓存,如果设置为 true,则会使用二级缓存。对于 select 元素,默认值为 true。 -->
<!-- useCache 属性只能控制是否使用二级缓存,它不能关闭一级缓存。一级缓存是 MyBatis 的默认行为,它总是开启的,无法关闭。 -->
<select id="queryActivityById" parameterType="cn.bugstack.mybatis.test.po.Activity" flushCache="false" useCache="true">
SELECT activity_id, activity_name, activity_desc, create_time, update_time
FROM activity
<trim prefix="where" prefixOverrides="AND | OR" suffixOverrides="and">
<if test="null != activityId">
activity_id = #{activityId}
</if>
</trim>
</select>
</mapper>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
其中 <cache > 标签有多个属性,这里一一介绍一下:
- type:可以指定自定义缓存,但是该类必须实现,而且是全类名
- eviction:缓存回收策略,默认为 LRU(Least Recently Used),策略介绍如下:
LRU:按照访问时间排序,最近未使用的数据优先清除。
FIFO:按照插入时间排序,先插入的数据先清除。
SOFT:基于垃圾回收算法,当系统内存不足时,会优先清理不常用的、占用内存较多的数据。
WEAK:弱引用机制,当 JVM 进行垃圾回收时,如果判断一个对象只被弱引用指向,则会将其回收。 - flushInterval:刷新间隔时间,表示多长时间刷新一次缓存,单位为毫秒,默认不刷新。
- size:缓存的大小,表示最多可以缓存多少个对象。
- readOnly:是否只读,默认为 false,表示启用缓存更新机制。
- blocking:是否启用阻塞,默认为 false,表示不启用。
flushInterval 默认情况下,MyBatis 采用基于 PerpetualCache (永久缓存) 的缓存实现方式,即缓存会一直保存在内存中,直到会话关闭时才被清除。而当我们使用基于 Ehcache 的缓存实现时,可以通过设置 flushInterval 属性控制缓存的刷新时间,即定时将缓存中的数据写入到磁盘或持久化存储中,以避免缓存过期、失效或内存溢出等问题。
当 Mybaits 启动后会读到二级缓存的配置,先会进行 <cache> 基础的解析,得到 XML 里面的属性值,其次用值信息组成一个 Cache 对象,并把这个 Cache 对象维护到全局配置 Configuration 中,该全局配置里面是维护一个 Map 结构的容器
// 开始解析
private void cacheElement(Element context) {
if (context == null) return;
// 基础配置信息,默认是永恒缓存
String type = context.attributeValue("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class<? extends Cache> typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
// 缓存队列 FIFO
String eviction = context.attributeValue("eviction", "FIFO");
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = Long.valueOf(context.attributeValue("flushInterval"));
Integer size = Integer.valueOf(context.attributeValue("size"));
boolean readWrite = !Boolean.parseBoolean(context.attributeValue("readOnly", "false"));
boolean blocking = !Boolean.parseBoolean(context.attributeValue("blocking", "false"));
// 解析额外属性信息;<property name="cacheFile" value="/tmp/xxx-cache.tmp"/>
List<Element> elements = context.elements();
Properties props = new Properties();
for (Element element : elements) {
props.setProperty(element.attributeValue("name"), element.attributeValue("value"));
}
// 构建缓存
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
// 构建Cache
public Cache useNewCache(Class<? extends Cache> typeClass,
Class<? extends Cache> evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
// 判断为null,则用默认值
typeClass = valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class);
evictionClass = valueOrDefault(evictionClass, FifoCache.class);
// 建造者模式构建 Cache [currentNamespace=cn.bugstack.mybatis.test.dao.IActivityDao]
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(typeClass)
.addDecorator(evictionClass)
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
// 添加缓存
configuration.addCache(cache);
// 给自己维护一个 cache 以便后续 MappedStatement 用到
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}
// 添加到 configuration全局配置维护的 caches中
public class Configuration {
// 缓存,存在Map里
protected final Map<String, Cache> caches = new HashMap<>();
public void addCache(Cache cache) {
caches.put(cache.getId(), cache);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
缓存解析过了,但是最主要的还是 <select> 标签着一些,标签上面描述了具体的缓存是否使用,缓存是否清除,所以还需要解析标签上的缓存信息,主要是 flushCache 和 useCache 这两个属性
// 解析操作
public void parseStatementNode() {
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
// 参数类型
String parameterType = element.attributeValue("parameterType");
Class<?> parameterTypeClass = resolveAlias(parameterType);
// 外部应用 resultMap
String resultMap = element.attributeValue("resultMap");
// 结果类型
String resultType = element.attributeValue("resultType");
Class<?> resultTypeClass = resolveAlias(resultType);
// 获取命令类型(select|insert|update|delete)
String nodeName = element.getName();
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = SqlCommandType.valueOf(nodeName.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH));
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
boolean flushCache = Boolean.parseBoolean(element.attributeValue("flushCache", String.valueOf(!isSelect)));
boolean useCache = Boolean.parseBoolean(element.attributeValue("useCache", String.valueOf(isSelect)));
// 获取默认语言驱动器
Class<?> langClass = configuration.getLanguageRegistry().getDefaultDriverClass();
LanguageDriver langDriver = configuration.getLanguageRegistry().getDriver(langClass);
// 解析<selectKey> step-14 新增
processSelectKeyNodes(id, parameterTypeClass, langDriver);
// 解析成SqlSource,DynamicSqlSource/RawSqlSource
SqlSource sqlSource = langDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, element, parameterTypeClass);
// 属性标记【仅对 insert 有用】, MyBatis 会通过 getGeneratedKeys 或者通过 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的值 step-14 新增
String keyProperty = element.attributeValue("keyProperty");
KeyGenerator keyGenerator = null;
String keyStatementId = id + SelectKeyGenerator.SELECT_KEY_SUFFIX;
keyStatementId = builderAssistant.applyCurrentNamespace(keyStatementId, true);
if (configuration.hasKeyGenerator(keyStatementId)) {
keyGenerator = configuration.getKeyGenerator(keyStatementId);
} else {
keyGenerator = configuration.isUseGeneratedKeys() && SqlCommandType.INSERT.equals(sqlCommandType) ? new Jdbc3KeyGenerator() : new NoKeyGenerator();
}
// 调用助手类
builderAssistant.addMappedStatement(id,
sqlSource,
sqlCommandType,
parameterTypeClass,
resultMap,
resultTypeClass,
flushCache,
useCache,
keyGenerator,
keyProperty,
langDriver);
}
// 把信息添加到 MappedStatement对象
public MappedStatement addMappedStatement(
String id,
SqlSource sqlSource,
SqlCommandType sqlCommandType,
Class<?> parameterType,
String resultMap,
Class<?> resultType,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
KeyGenerator keyGenerator,
String keyProperty,
LanguageDriver lang
) {
// 给id加上namespace前缀:cn.bugstack.mybatis.test.dao.IUserDao.queryUserInfoById
id = applyCurrentNamespace(id, false);
//是否是select语句
boolean isSelect = sqlCommandType == SqlCommandType.SELECT;
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder = new MappedStatement.Builder(configuration, id, sqlCommandType, sqlSource, resultType);
statementBuilder.resource(resource);
statementBuilder.keyGenerator(keyGenerator);
statementBuilder.keyProperty(keyProperty);
// 结果映射,给 MappedStatement#resultMaps
setStatementResultMap(resultMap, resultType, statementBuilder);
// 维护缓存信息
setStatementCache(isSelect, flushCache, useCache, currentCache, statementBuilder);
MappedStatement statement = statementBuilder.build();
// 映射语句信息,建造完存放到配置项中
configuration.addMappedStatement(statement);
return statement;
}
// 给Statement添加缓存信息
private void setStatementCache(
boolean isSelect,
boolean flushCache,
boolean useCache,
Cache cache,
MappedStatement.Builder statementBuilder) {
flushCache = valueOrDefault(flushCache, !isSelect);
useCache = valueOrDefault(useCache, isSelect);
statementBuilder.flushCacheRequired(flushCache);
statementBuilder.useCache(useCache);
statementBuilder.cache(cache);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
在具体的 addMappedStatement 的时候,可以看到会得到一个 MappedStatement 对象,该对象就是封装了 SQL 标签的所有信息,在 setStatementCache 方法中,不仅只把 flushCache和useCache 进行了设置,额外的还带有一个 cache ,该 cache 就是在调用 useNewCache 方法,内部赋值的 currentCache ,他们的方法是在同一个类中,因此可以使用。这样 MappedStatement 对象也就拥有了 <cache> 标签的能力,到此解析完毕
# 准备
和一级缓存一样,都是在 openSession 的时候去做实例化,但是不同的是,二级缓存会在一级缓存上进行一个装饰,并且首要会判断是否允许开启二级缓存。
if (cacheEnabled) {
executor = new CachingExecutor(executor);
}
2
3
CachingExecutor 接收 executor ,并对其进行包装,内部方法依然调用的是 BaseExecutor 的相关方法。 CachingExecutor 内部还维护了 TransactionalCacheManager 事务缓存管理器,该管理器内部维护 Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> , TransactionalCache 内部又维护了 Cache 以及 entriesMissedInCache 和 entriesToAddOnCommit
# 执行
public class CachingExecutor implements Executor {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(CachingExecutor.class);
private Executor delegate;
// 事务缓存管理器
private TransactionalCacheManager tcm = new TransactionalCacheManager();
public CachingExecutor(Executor delegate) {
this.delegate = delegate;
delegate.setExecutorWrapper(this);
}
@Override
public int update(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter) throws SQLException {
return delegate.update(ms, parameter);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null) {
flushCacheIfRequired(ms);
if (ms.isUseCache() && resultHandler == null) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<E> list = (List<E>) tcm.getObject(cache, key);
if (list == null) {
list = delegate.<E>query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
// cache:缓存队列实现类,FIFO
// key:哈希值 [mappedStatementId + offset + limit + SQL + queryParams + environment]
// list:查询的数据
tcm.putObject(cache, key, list);
}
// 打印调试日志,记录二级缓存获取数据
if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && cache.getSize() > 0) {
logger.debug("二级缓存:{}", JSON.toJSONString(list));
}
return list;
}
}
return delegate.<E>query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// 1. 获取绑定SQL
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
// 2. 创建缓存Key
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
@Override
public Transaction getTransaction() {
return delegate.getTransaction();
}
@Override
public void commit(boolean required) throws SQLException {
delegate.commit(required);
tcm.commit();
}
@Override
public void rollback(boolean required) throws SQLException {
try {
delegate.rollback(required);
} finally {
if (required) {
tcm.rollback();
}
}
}
@Override
public void close(boolean forceRollback) {
try {
if (forceRollback) {
tcm.rollback();
} else {
tcm.commit();
}
} finally {
delegate.close(forceRollback);
}
}
@Override
public void clearLocalCache() {
delegate.clearLocalCache();
}
@Override
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
return delegate.createCacheKey(ms, parameterObject, rowBounds, boundSql);
}
@Override
public void setExecutorWrapper(Executor executor) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("This method should not be called");
}
private void flushCacheIfRequired(MappedStatement ms) {
Cache cache = ms.getCache();
if (cache != null && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
tcm.clear(cache);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
public class TransactionalCacheManager {
private Map<Cache, TransactionalCache> transactionalCaches = new HashMap<>();
public void clear(Cache cache) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).clear();
}
/**
* 得到某个TransactionalCache的值
*/
public Object getObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key) {
return getTransactionalCache(cache).getObject(key);
}
public void putObject(Cache cache, CacheKey key, Object value) {
getTransactionalCache(cache).putObject(key, value);
}
/**
* 提交时全部提交
*/
public void commit() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.commit();
}
}
/**
* 回滚时全部回滚
*/
public void rollback() {
for (TransactionalCache txCache : transactionalCaches.values()) {
txCache.rollback();
}
}
private TransactionalCache getTransactionalCache(Cache cache) {
TransactionalCache txCache = transactionalCaches.get(cache);
if (txCache == null) {
txCache = new TransactionalCache(cache);
transactionalCaches.put(cache, txCache);
}
return txCache;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
public class TransactionalCache implements Cache {
private Cache delegate;
// commit 时要不要清缓存
private boolean clearOnCommit;
// commit 时要添加的元素
private Map<Object, Object> entriesToAddOnCommit;
private Set<Object> entriesMissedInCache;
public TransactionalCache(Cache delegate) {
// delegate = FifoCache
this.delegate = delegate;
// 默认 commit 时不清缓存
this.clearOnCommit = false;
this.entriesToAddOnCommit = new HashMap<>();
this.entriesMissedInCache = new HashSet<>();
}
@Override
public String getId() {
return delegate.getId();
}
@Override
public int getSize() {
return delegate.getSize();
}
@Override
public Object getObject(Object key) {
// key:CacheKey 拼装后的哈希码
Object object = delegate.getObject(key);
if (object == null) {
entriesMissedInCache.add(key);
}
return clearOnCommit ? null : object;
}
@Override
public void putObject(Object key, Object object) {
entriesToAddOnCommit.put(key, object);
}
@Override
public Object removeObject(Object key) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void clear() {
clearOnCommit = true;
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
}
public void commit() {
if (clearOnCommit) {
delegate.clear();
}
flushPendingEntries();
reset();
}
public void rollback() {
unlockMissedEntries();
reset();
}
private void reset() {
clearOnCommit = false;
entriesToAddOnCommit.clear();
entriesMissedInCache.clear();
}
/**
* 刷新数据到 MappedStatement#Cache 中,也就是把数据填充到 Mapper XML 级别下。
* flushPendingEntries 方法把事务缓存下的数据,填充到 FifoCache 中。
*/
private void flushPendingEntries() {
for (Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry : entriesToAddOnCommit.entrySet()) {
delegate.putObject(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
if (!entriesToAddOnCommit.containsKey(entry)) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}
private void unlockMissedEntries() {
for (Object entry : entriesMissedInCache) {
delegate.putObject(entry, null);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
其实上面饶了一圈下来,最终操作的是 MappedStatement 维护的 Cache 对象, MappedStatement 是被全局 Configuration 在缓存的,所以查询结束不会清除 MappedStatement 对象和缓存信息,只有当触发 update,commit,rollback 等才会清除 MappedStatement 里维护的缓存信息
