 Flink CEP编程
Flink CEP编程
# 简介
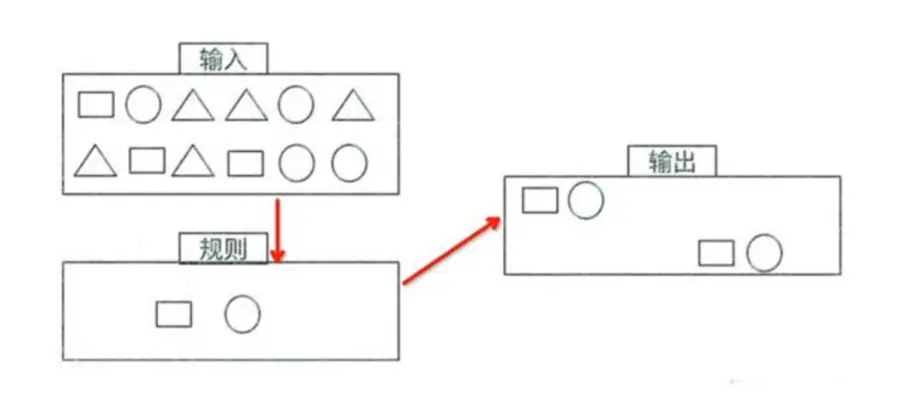
CEP(Complex Event Processing)复杂时间处理库,用于在流中筛选符合某种复杂模式的事件。CEP 允许在无休止的事件流中检测事件模式,让我们有机会掌握数据中重要的部分;一个或多个由简单事件构成的事件流通过一定的规则匹配,然后输出用户想得到的数据。
我的输入有多种类型的数据,我想通过规则的制定,让圆形后面的数据必须为四边形。
# Pattern API
Flink CEP 提供了 Pattern API,用于对输入流数据进行复杂事件规则定义,用来提取符合规则的事件序列。
Pattern
// begin开始条件的命名,where为条件
.<EventData>begin("first").where(new SimpleCondition<EventData>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 3;
}
})
// 接着上个数据的条件,也要符合下个数据的条件,相连的
.next("second")
// 当前事件的子类型,EventData下或许有多个子类型
.subtype(SubEventData.class)
.where(new SimpleCondition<EventData>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 3;
}
})
// 跟在后满,不一定非要在下一个(next)数据满足条件,只要后续有满足的
.followedBy("end")
.where(new SimpleCondition<EventData>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 6;
}
})
// 时间限制,在多长时间范围内
.within(Time.seconds(2));
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
# 个体模式(Individual Patterns)
组成复杂规则的每一个单独的模式定义,就是 “个体模式”。
// 符合where条件的3个连续事件
start.times(3).where(new SimpleCondition<EventData >(){...})
2
个体模式可以包括单例(singleton)模式和循环(looping)模式,单例模式只接收一个事件,而循环模式可以接收多个。
# 量词(Quantifier)
可以在一个个体模式后追加两次,也就是制定循环次数。
// 匹配出现4次
start.times(4)
// 连续出现3次
start.times(3).consecutive()
// 匹配出现0或4次
start.times(4).optional
// 匹配出现2,3或者4次
start.times(2,4)
// 匹配出现2,3或者4次,并且尽可能多地重复匹配
start.times(2,4).greedy
// 匹配出现1次或多次
start.oneOrMore
// 匹配出现0次、2次或多次,并且尽可能多的重复匹配
start.timesOrMore(2).optional.greedy
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 条件(Condition)
每个模式都需要指定触发条件,作为模式是否接受事件进入的判断一句;CEP 中的个体模式主要通过调用 .where () .or () .until () 来指定条件;按不同的调用当时,可以分成以下几类:
- 简单条件(Simple Condition),通过 .where () 方法对事件中的字段进行判断筛选,决定是否接受该事件
start.where(new SimpleCondition<EventData >(){
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 3;
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
- 组合条件(Combining Condition),将简单条件惊醒合并;.or () 方法表示或,逻辑相连,想多个条件就 where 后面可以在加 where
// 两个事件只要一个满足
pattern.where(event => ... ).or(event => ... )
2
- 终止条件(Stop Condition),如果使用了 oneOrMore 或者 oneOrMore.optional,建议使用 .until () 作为终止条件,以便清理状态
- 迭代条件(Iterative Condition),能够对模式之前所有接收的事件进行处理,在类里调用上下文 ctx.getEventsForPattern ("name")
.where(new IterativeCondition<EventData>(){...})
# 组合模式(Combining Patterns,也叫模式序列)
很多个体模式组合起来,就形成了整个模式序列,模式序列必须以一个 “初始模式” 开始。
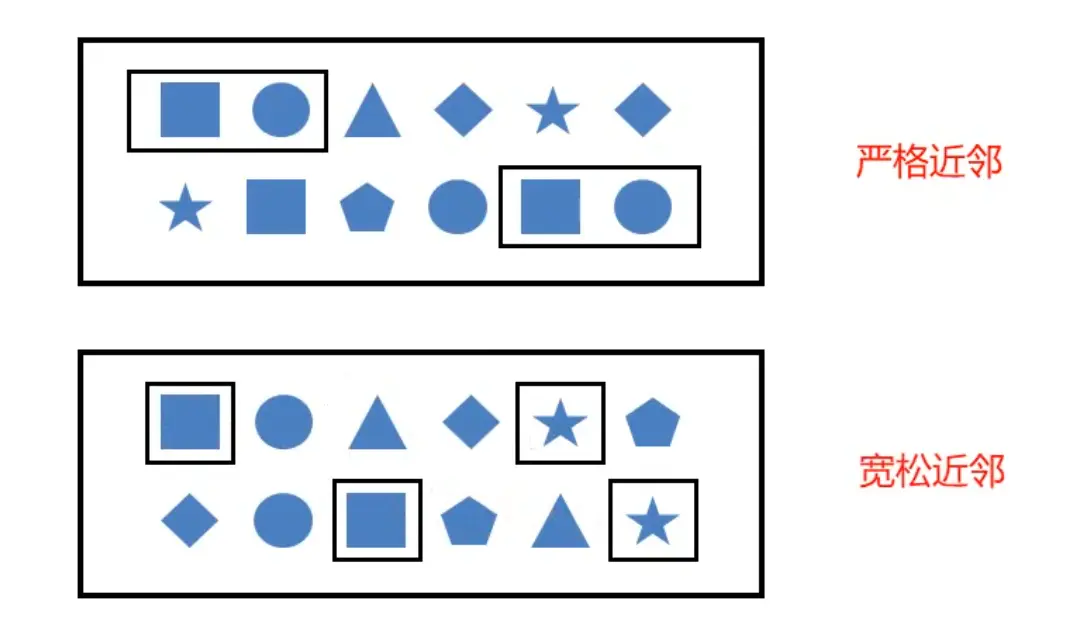
严格近邻(Strict Contiguity)
所有事件按照严格的顺序出现,中间没有任何不匹配的事件,由 .next () 指定,例如对于模式 "a next b",事件序列 [a,c,b1,b2] 没有匹配。宽松近邻(Relaxed Contiguity)
允许中间出现不匹配的事件,由 .followedBy () 指定,例如对于模式 "a followedBy b",事件序列 [a,c,b1,b2] 匹配为 '{a,b1}'非确定性宽松近邻(Non-Deterministic Relaxed Contiguity)
进一步放宽条件,之前已经匹配过的事件也可以再次使用,由 .followedByAny () 指定,例如对于模式 "a followedByAny b",事件序列 [a,c,b1,b2] 匹配为 '{a,b1}','{a,b2}'
除了以上模式序列外,还可以定义 ” 不希望出现某种近邻关系 “:.notNext () 不想让某个事件严格近邻前一事件发生;.notFollowedBy () 不想让某个事件在两个事件之间发生
所有模式序列必须以 .begion () 开始
模式序列不能以 .notFollowedBy () 结束
"not" 类型的模式不能被 optional 所修饰
此外,还可以为模式指定时间约束,用来要求在多长时间内匹配有效 next.within (Time.seconds (10))
# 模式组(Groups of patterns)
将一个模式序列作为条件嵌套在个体模式里,成为一组模式。
# 模式的检测
指定要查找的模式序列后,就可以将其应用于输入流以检测潜在匹配;调用 CEP.pattern (),给定输入流和模式,就能得到一个 PatternStream
DataStream<DataEvent> input = ...
Pattern<DataEvent> pattern = Pattern.<DataEvent>begin("start").where(...)...
PatternStream<DataEvent> patternStream = CEP.pattern(input,pattern);
2
3
# 匹配事件的提取
public OUT select(Map<String,List<IN>> pattern) throws Exception {
IN startEvent = pattern.get("start").get(0);
IN startEvent = pattern.get("end").get(0);
return new OUT(startEvent,endEvent)
}
2
3
4
5
# 超时事件的提取
当一个模式通过 within 关键字定义了检测窗口时间时,部分事件序列可能因为超过窗口长度而被丢弃;为了能够处理这些超时的部分匹配,select 和 flatselect API 调用允许指定超时处理程序。
超时处理程序会接收到目前位置由模式匹配到的所有事件,由一个 OutputTag 定义接收到的超时事件序列
PatternStream<DataEvent> patternStream = CEP.pattern(input,pattern);
OutputTag<String> outputTag = new OutputTag<String>("sid-output"){};
SingleOutputStreamOperator<ComplexEvent> flatResult = patternStream.flatSelect(
outputTag,
new PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<Event,TimeoutEvent>(){...},
new PatternFlatTimeoutFunction<Event,ComplexEvent>(){...}
);
DataStream<TimeoutEvent> timeoutFlatResult = flatResult .getSideOutput(outputTag)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
# 实际应用
<!-- cep 编程所需 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flink</groupId>
<artifactId>flink-cep_2.12</artifactId>
<version>1.12.2</version>
</dependency>
2
3
4
5
6
找出两个相邻事件 (连续两个) num > 3 的,发生时间在 2s 内的
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(4);
DataStream<String> dataStream = env.readTextFile("D:\\workspace\\middleware\\flink\\flink-test\\src\\main\\resources\\hello.txt");
// 数据转换
DataStream<EventData> stream = dataStream.map(new MapFunction<String, EventData>() {
@Override
public EventData map(String value) throws Exception {
String[] strs = value.split(",");
return new EventData(
strs[0],
Long.valueOf(strs[1]),
strs[1],
Integer.valueOf(strs[3])
);
}
// 添加时间水印
}).assignTimestampsAndWatermarks(
// 时间是升序有序
WatermarkStrategy.<EventData>forBoundedOutOfOrderness(Duration.ofSeconds(3))
.withTimestampAssigner(new SerializableTimestampAssigner<EventData>() {
@Override
public long extractTimestamp(EventData element, long recordTimestamp) {
return element.getEventTime()*1000L;
}
})
);
// 业务逻辑:找出两个 相邻事件num > 3 的,发生时间在2s内的
// 定义一个匹配模式
Pattern<EventData, EventData> within = Pattern.<EventData>begin("first").where(new SimpleCondition<EventData>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 3;
}
}).next("second").where(new SimpleCondition<EventData>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 3;
}
// 时间限制,在多长时间范围内
}).within(Time.seconds(2));
// 将匹配模式应用到数据流上
PatternStream<EventData> pattern = CEP.pattern(stream.keyBy(EventData::getId), within);
// 检出符合匹配条件的复杂事件,进行转换处理,得到想要的数据
pattern.select(new PatternSelectFunction<EventData, Map<String,String>>() {
@Override
public Map<String,String> select(Map<String, List<EventData>> map) throws Exception {
return new HashedMap(2){{
put("first",map.get("first").get(0).getData());
put("second",map.get("second").get(0).getData());
}};
}
}).print();
env.execute("test");
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
连续 (严格近邻模式) 10 个 num > 3 的,发生时间在 2s 内的
Pattern<EventData, EventData> within = Pattern.<EventData>begin("first").where(new SimpleCondition<EventData>() {
@Override
public boolean filter(EventData value) throws Exception {
return value.getNum().intValue() > 3;
}
})
// consecutive连续(严格近邻模式) times10次
.times(10).consecutive()
// 时间限制,在多长时间范围内
.within(Time.seconds(2));
// 将匹配模式应用到数据流上
PatternStream<EventData> pattern = CEP.pattern(stream.keyBy(EventData::getId), within);
// 检出符合匹配条件的复杂事件,进行转换处理,得到想要的数据
pattern.select(new PatternSelectFunction<EventData, Map<String,String>>() {
@Override
public Map<String,String> select(Map<String, List<EventData>> map) throws Exception {
return new HashedMap(2){{
put("first",map.get("first").get(0).getData());
put("second",map.get("first").get(1).getData());
}};
}
}).print();
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
